Living and Non-Living Organisms
- Living organisms, including humans, plants, and animals, require food for survival and existence.
- These organisms can reproduce, react to their environment, and easily adapt to changes.
- Additionally, living organisms engage in respiration and excretion.
Cells
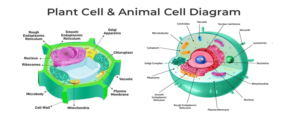
Cells are considered as the primary units that makes up any living organism, also described as the building blocks of life.
- A cell comprises three primary components:
- A thin outer layer known as the cell membrane.
- A central spherical structure called the nucleus.
- A jelly-like substance surrounding the nucleus, referred to as the cytoplasm.
Single and Multi-Cellular Organisms
- Organisms composed of a single cell are termed unicellular organisms, such as Amoeba.
- Organisms that consist of multiple cells are classified as multicellular organisms.
- All humans, plants, and animals fall under the category of multicellular organisms.
Nutrition
Nutrition refers to the process by which an organism ingests food and utilizes it within its body.
- Nutrition is crucial as the nutrients derived from consumed food enable living organisms to develop and grow.
- It also plays a vital role in repairing damaged tissues and organs.
- Furthermore, nutrition provides the energy necessary for various bodily functions.
Autotrophs and Heterotrophs
Organisms that are able to synthesis their own food are known as autotrophs.
- An example of autotrophs is plants, which synthesize their food using carbon dioxide, water, and light energy.
Organisms that depend on others for their food, typically consuming ready-made food produced by autotrophs, are referred to as heterotrophs.
- Animals and humans exemplify heterotrophs, as they rely on plants for sustenance in numerous ways.
Photosynthesis
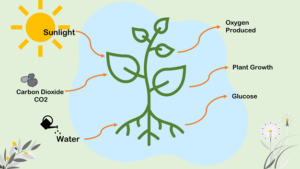
The process by which green plants synthesize their own food are known as photosynthesis.
- This process predominantly occurs in the leaves of plants.
The process necessitates the presence of chlorophyll, a green pigment, along with sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
Organelles are minute structures within a cell that perform essential functions vital to cellular operations. These structures are located in the cytoplasm. For instance, chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for conducting photosynthesis.
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found in plant cells. They house chlorophyll, the green pigment that facilitates the photosynthesis process in plants.
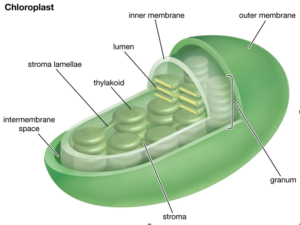
Chlorophyll is the pigment that enables food synthesis in green plants. It imparts a green hue to the plant tissues and is predominantly located in the leaves. Chlorophyll is contained within the chloroplasts.
Photosynthesis occurs in the leaves, which serve as the “food factory” for plants. Carbon dioxide enters the leaves through small openings known as stomata. Water molecules and the necessary minerals are transferred from the roots to the leaves via the stem. Chlorophyll enables the leaves to harness sunlight energy to produce food using carbon dioxide, water, and minerals; as a by-product oxygen will be released. The overall equation can be represented as follows:
carbon dioxide + water —> glucose + oxygen + water

Plants require mineral nutrients from the soil to produce their own food and to support various vital processes. It is essential to regularly enrich the soil with nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to promote healthy plant growth. There are 17 key nutrients necessary for plants, categorized into six macronutrients and the remaining as micronutrients. Macronutrients are needed in larger amounts, while micronutrients are required in trace quantities.
Alternative Nutritional Methods.
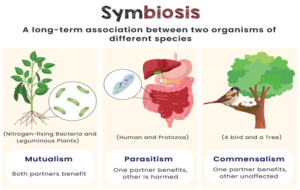
1. Symbiotic Relationship
Organisms that coexist and share both their habitat and nutrients are described as being in a symbiotic relationship.
- Certain fungi inhabit the roots of trees.
- The tree supplies nutrients to the fungus, which in turn assists the tree in absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. This mutual association benefits both the fungi and the tree.
- A well-known example is Rhizobium bacteria, that reside in the root nodules of leguminous plants.
- They supply the plant with nitrogen, which they fix, while receiving shelter and nourishment from the plant.
2. Rhizobium
- Rhizobium is a type of bacteria that transforms atmospheric nitrogen into a soluble form that plants can utilize (nitrogen fixation).
- It typically resides in the roots of leguminous plants such as peas, chickpeas, and mung beans, playing a crucial role in providing these plants with a substantial nitrogen source.
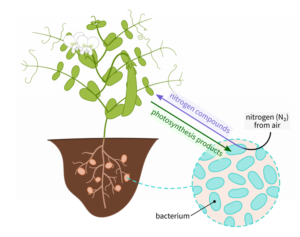
3. Nitrogen Fixation
- Nitrogen is a vital nutrient necessary for soil health and plant growth, but it is not readily available in the atmosphere.
The process of conversion in which the nitrogen gas is converted into utilizable form for plants and other living organisms is known as nitrogen fixation.
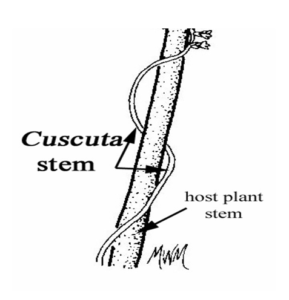
4. Parasites
A parasite is a heterotrophic organism that relies entirely on another organism for sustenance.
- The organism that the parasite attaches to is referred to as the host.
- In this relationship, the host is deprived of essential nutrients needed for its own growth, as these nutrients are consumed by the parasite.
- For instance, Cuscuta (commonly known as dodder) is a non-green plant that extracts pre-formed food from the host plant on which it grows.
5. Saprotrophs
Organisms that depend on dead and decaying organic matter for their nutrition are termed saprotrophs.
- This nutritional strategy is known as saprotrophic nutrition.
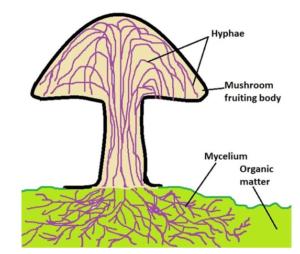
- An example of saprotrophs includes fungi.
- Fungi release digestive enzymes onto dead and decaying matter, breaking it down into a solution.
- They then absorb the nutrients from this solution.
6. Insectivorous Plants
Plants that consume insects are referred to as insectivorous plants.
- These plants possess green foliage and perform photosynthesis.
- However, they thrive in soils that are deficient in nitrogen.
- To obtain the necessary nitrogen, they capture and digest insects.
- The structures of these insectivorous plants are adapted to lure and trap insects.
- Some of the common examples include the pitcher plant and the Venus flytrap.

FYI
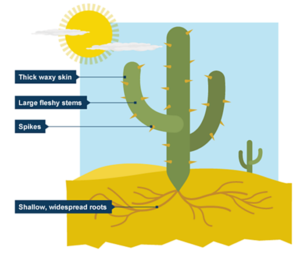
Cactus Plants
- In most green plants, the majority of photosynthesis occurs in the leaves.
- Conversely, in certain desert plants, this process takes place in the stems and even the branches.
- Cacti, which inhabit arid environments, have leaves that are transformed into spines to minimize water loss through transpiration.
- As a result, their green stems facilitate the process of photosynthesis.